




Resin material can include both solid and highly viscous materials, but commonly refers to liquids which harden based on heat, setting agents, or light. Typically, modified or synthetic resins are used for manufacturing – they can be produced from natural components with additives or consist of artificial polymers. It is also used for 3D printing.
The main use of resin is to be a glue - to transfer stress between the fibers, clasp them together and protect from outside factors. The first resins have been found in nature - in plants, bugs or trees - amber or shellac are some of the examples of natural resins. These natural resins are used in some products but usually, they are flammable and fusible, may appear soluble in liquids, which makes them not suitable for some applications.
Order in Resin



All resins have the ability to harden under certain conditions - by mixing with a setting agent, heated, or exposed to light. The latter method is used for resin 3D printing. Such materials are highly viscous liquids before solidifying. The range of synthetic resins is huge and includes resins created from thermoplastics like ABS, Nylon, and Polypropylene. Some of these are referred to as resins only in their liquid form – after curing, they are simply called plastics or elastomers. Some resins after hardening can’t be melted or re-used. Different types of resins exist depending on their chemical compounds which define its properties: silicones, epoxies, acrylics, alkyds, and more.
There is a huge variety of different resin materials, both natural and synthetic. Resins consist of long chains of monomers, which form cross-link bonds during the curing process.
Typically resins are divided into thermosets and thermoplastics based on whether or not the hardening reaction can be reversed. Widely used thermoplastic resins include ABS, polyethylene, polystyrene, and polycarbonate. Most common thermoset resins are polyester, vinyl ester, epoxy, and polyurethane.
Thermoplastic resins are basically the ones that can be melted and then hardened once cooled. Within the molecule chain of such resins, there are extremely strong bonds between molecules. Thermosets, on the contrary, undergo a non-reversible reaction resulting in a hard end product. It is determined by the process called polymerization or cross-linking which takes place in such materials caused by the use of a catalyst, heat or a combination of the two.
Production of artificial resins starts from a so-called cracking process, which means that different types of hydrocarbons are heated up to separate molecules. Then polymer compounds are built in order to create a specific resin.
Properties can be improved to certain levels depending on the resin's composition. But we included several quite popular resins into a list to demonstrate how different can these materials be once hardened.
| Resin | Properties | Max.Temperature (ºC) |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Glossy finishing, good shock resistance. | 100 |
| Epoxy | Great physical and chemical properties. Easy to cast with. | 200 |
| Nylon | Great wear resistance. | 140 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Transparent. Withstands acid and shock. | 130 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Great mechanical strength | 140 |
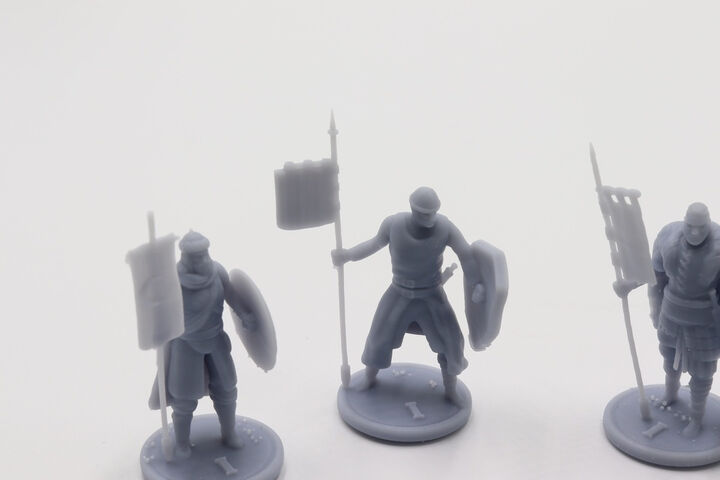
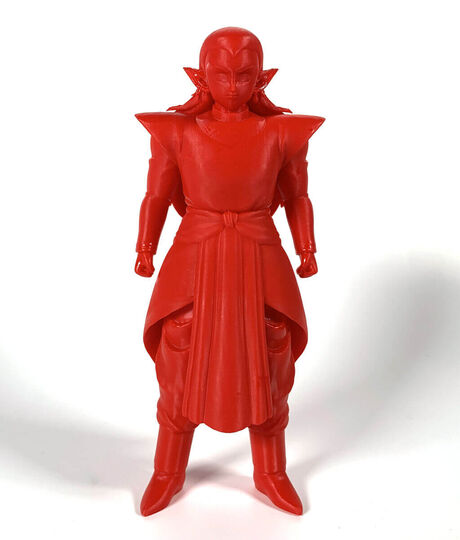
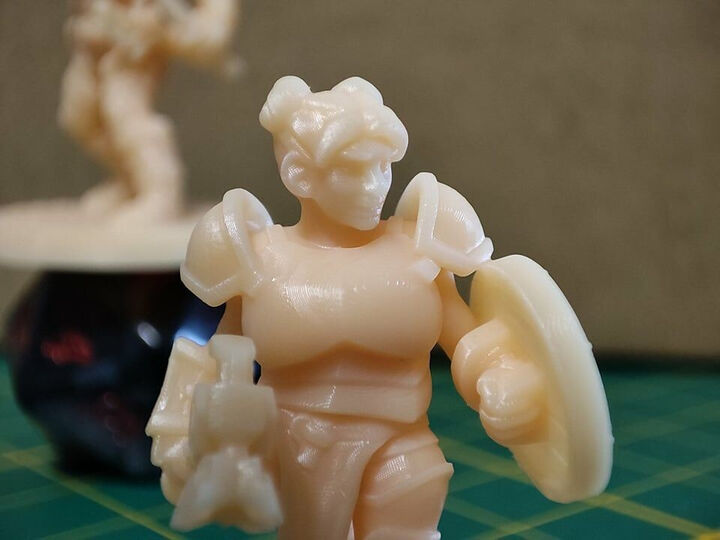
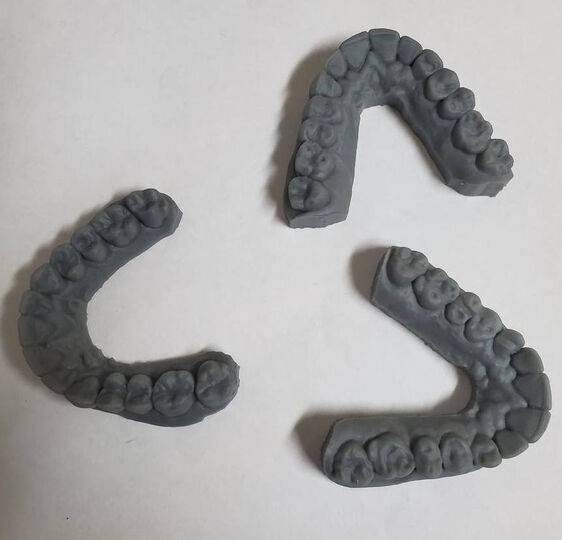
In 3D printing, resins are a family of photopolymers that consist of a photoinitiator and different monomers. These materials react under UV-light, daylight or laser beam energy that changes their state from a liquid to a solid structure. 3D printers direct light sources to certain areas that need to be solidified and create a part, layer-by-layer, or in the case of MJP technology, resin drops are applied all together and cured after each layer.
Resins are used in casting for low-volume production, props, in the medical industry, and more. It requires molds, which are filled with liquid resin and hardens inside polymerizing. Some resins are easy to use and compatible with silicone or DIY molds, so even hobbyists can use them without special tooling to produce parts. The liquid nature of resin material also allows mixing it with additives for improving its properties and easier removal of molds.
Resin casting is a manufacturing method widely used for low volume production by professionals and hobbyists. The general idea is to fill in a mold with a liquid resin, leave it until the material hardens and then release a product from its mold.
Commonly flexible molds are used, which can be made from latex or silicone rubber, to make releasing the cast easier. Such molds can be used multiple times depending on their condition but they tend to have their own limits that don’t allow to use resins casting for big batches. Some simple molds for one-time use can also be made from available materials like plastic folders, wood pieces and more.
For mechanical and automotive parts, when all the details should be transferred to the casted part perfectly, special resin grades and mold materials are used to cut down shrinkage and inaccuracy.
Resins aren’t commonly used in CNC machining since they require a solid material to work with. Hardened resins like ABS, epoxy, Nylons and others can be machined as they are already plastics. However, on the market, there are some rare CNC machines that can combine paste extrusion of resins with milling operations. Resins, in this case, are typically used as a coating for other materials and they can be placed and then machined with the same CNC machine in one go.
Resins have numerous applications starting from jewelry making to manufacturing parts for sports cars. Different resins can be used by themselves as a base or as a gluing agent for materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass and more.
Resins are widely used in building as adhesives, coatings or as a construction material when a strong bond is required. For example, for laminated wood construction. Resins are also popular in the decoration of self-leveling floors and architectural surfaces enabling to use of recycled materials.
All Comments (0)